INTRODUCTION
The homeostasis of adult structures and tissues that undergo cons tant turnover depends on the supply of regenerating cells1,2. For the corneal epithelium, the healing process involves the proliferation of transient amplifying cells (TACs) derived from the differentiation of stem cells (SCs) located in the limbal basal epithelium3-9 (Figure 1).
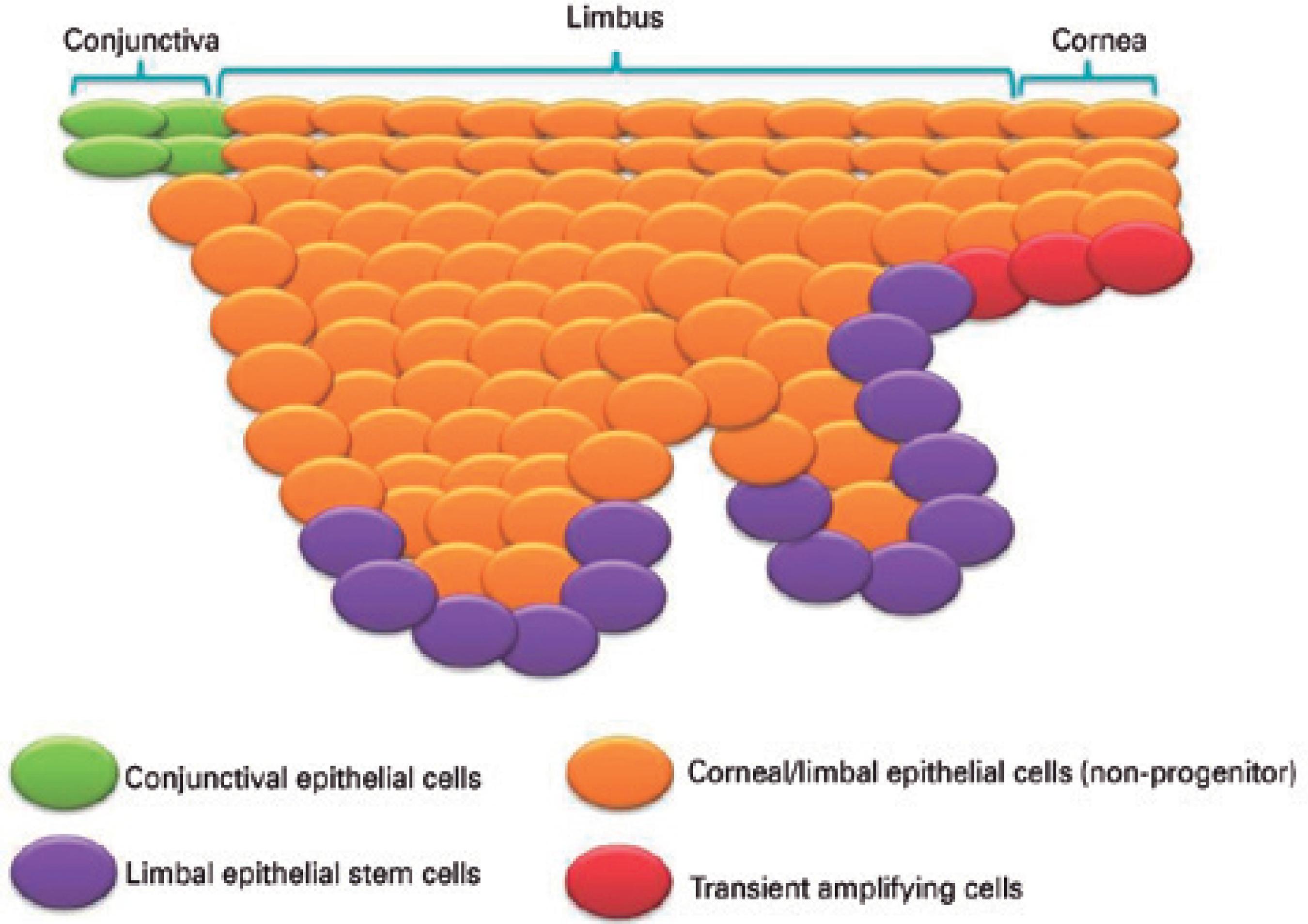
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the limbus and surrounding epithelium region. Limbal stem cells are located in the limbal basal epithelium, with other cell types, such as the transient amplifying cells, found in the vicinity of this epithelial layer.
Destruction of the SC and TAC populations (i.e., the progenitor cells) results in limbal deficiency, which has many consequences for the morphofunctionality of the ocular surface10,11. Limbal deficiency is difficult to manage, especially when it affects both eyes and/or more than half of the cornea10-12. The most commonly used approaches for treating these cases are based on replacing the lost SCs and restoring the stromal microenvironment10. These approaches can involve the transplantation of limbal grafts, non-limbal epithelial SCs, intact or denuded amniotic membrane, free-carrier corneal epi thelial sheets, or tissue-engineered grafts constructed in vitro from limbal epithelial stem or progenitor cells and matrices or substrates, such as the amniotic membrane or fibrin13-20.
The transplantation of substrates colonized by cultured limbal epithelial cells has gained scientific and media popularity in recent years. However, several longstanding problems associated with the development of limbal epithelial SC-based tissue grafts for corneal surface reconstruction, and deriving the benefits from these, remain to be solved. For example, there is limited understanding of the biological and technical variables that influence the survival and viability of limbal cells and grafted tissue and matrix; the success rate of procedures varies considerably between studies, with long-term outcomes poorly defined; and the therapeutic effectiveness of bioengineered corneal surface grafts is dependent on the causal agent of limbal deficiency and has yet to be extensively evaluated by large-cohort studies and meta-analysis.
The clinical applications of bioengineered corneal surface grafts go beyond our understanding of the stimuli and mechanisms involved in the modulation of limbal epithelial SCs and TACs. Some re searchers have pointed out that the lack of a specific immunomarker hampers the in situ investigation of SCs and their interaction with the niche. In our opinion, the progression of knowledge on limbal epithelial progenitor cells has been also stifled by the constant repetition of hypotheses and methods employed in laboratory research.
In 2007, Li et al.21 published a notable review that summarized the latest findings at that time related to niche regulation of limbal epithelial SCs. However, the articles they reviewed, and most reports published since, have only poorly explored the regulation of limbal epithelial SCs and TACs by biophysical or mechanical cues related to the supramolecular organization of extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Biophysical cues occur in all body tissues (both adult and embryonic) and are essential to maintaining normal development and function22-28.
The objective of this review is to offer new supramolecular and biophysics perspectives on the niche regulation of limbal epithelial SCs and the differentiation of their progeny. Our aim has not been to provide a comprehensive and conclusive review; rather, because data on many of the concepts presented here are currently insufficient, our intention is to explore the issues and to encourage future research.
The limbal epithelial stem cell extracellular niche: evidence of liquid crystalline supramolecular organization
The human limbal epithelial SCs reside in a three-dimensional microenvironment, referred to as a niche, located at the limbal palisades of Vogt, an area which is dark pigmented, vascularized, innervated, and infiltrated with suppressor T-lymphocytes and Langerhans cells22,29-35. The basement membrane (BM) of the limbal palisades of Vogt has a unique structure, which results from the expression of molecules that are absent in the corneal BM such as integrin alpha-936, N-cadherin without connexin37, and laminin α2β2 chains38. In contrast to the cornea, the limbal BM is undulating, with pegs of stroma that extend upward and are fenestrated22,29-35. Because of this unique structure, many excellent papers have suggested a close interaction between limbal stroma and basal epithelium22,29-39.
It is widely accepted that the microenvironmental regulation of limbal epithelial SCs involves bi-directional interaction (i.e., biocybernetic regulation) of the cells with the BM and stroma, and is closely related to stemness, differentiation, and the proliferation of TACs22. Conversely, a recent study40 showed that corneal epithelial cells are able to self-organize in a cohesive centripetal growth pattern in the absence of external regulation. It should be noted, however, that three requirements are needed for this: SCs located circumferentially, a limited number of cell divisions, and cell mobility in response to population pressure40.
Several authors22,29-35,41 have suggested that the limbal epithelial SCs and their progeny are modulated differently in the presence or absence of limbal stroma and BM. Experiments that combined isolated limbal and corneal epithelial sheets with either limbal or corneal stroma showed that intrastromal invasion of limbal epithelial progenitor cells occurred only in the limbal region and not in the corneal region42. It appears that the limbal stroma is capable of downregulating the expression of cytokeratin 3 (considered a corneal epithelial-specific marker) and connexin 43 (considered a putative negative marker of SCs), and of causing the de-differentiation of the corneal epithelial cells into cells with nearly all features of SCs42. In addition, confocal microscopy evaluations of keratoconus corneas showed that the epithelial cells were affected by changes in BM and the stroma43,44. There is evidence that corneal wounding may modulate the differentiation of corneal epithelial cells due to a disrupted BM, resulting in the de-differentiation of corneal cells41. Thus, it is possible that changes in the BM provide an altered niche that enables the central corneal basal epithelium to assume a phenotype resembling that of limbal epithelial SCs and TACs41. In addition, the etiologic association of limbal deficiency with many diseases that cause stromal dysfunction10,11, such as aniridia, neurotrophic keratopathy, keratitis associated with multiple endocrine deficiencies, chronic limbitis, and congenital erythrokeratodermia, supports the concept that the limbal epithelial SCs are modulated (at least in part) by the stroma and the BM.
The mechanisms by which the components of limbal stroma and BM can affect the limbal epithelium are not fully understood, and many approaches have been taken to extend knowledge in this field (Figure 2). Studies of the limbal epithelial SC niche have used transgenic mice null for the expression of various genes (such as Dkk2 and Pax6) that govern oculogenesis45,46. In addition, there has been extensive study of various signaling pathways involved with the development, healing, and tumorigenesis of several tissues, including the PI3K/Akt, Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, Sonic hedgehog, TGF-β/BMP, and Ras/MAPK pathways22,47-50. Limbal epithelial SC-related adhesion molecules have been investigated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction arrays51. Much attention also has been fo cused on the heterogeneity and regulatory function of growth and survival factors, cytokines, enzymes, and the small permeable molecules thought to be secreted by the limbal stromal cells, as well as on the biochemical interactions of limbal epithelial SCs with other niche cells and with oligomers of ECM components52. More recently, it has been suggested that the HC-HA/PTX3 complex, formed from hyaluronan, heavy chain 1 of the inter-α-trypsin inhibitor, and pentraxin 3, could be related to the quiescence of limbal epithelial SCs53.
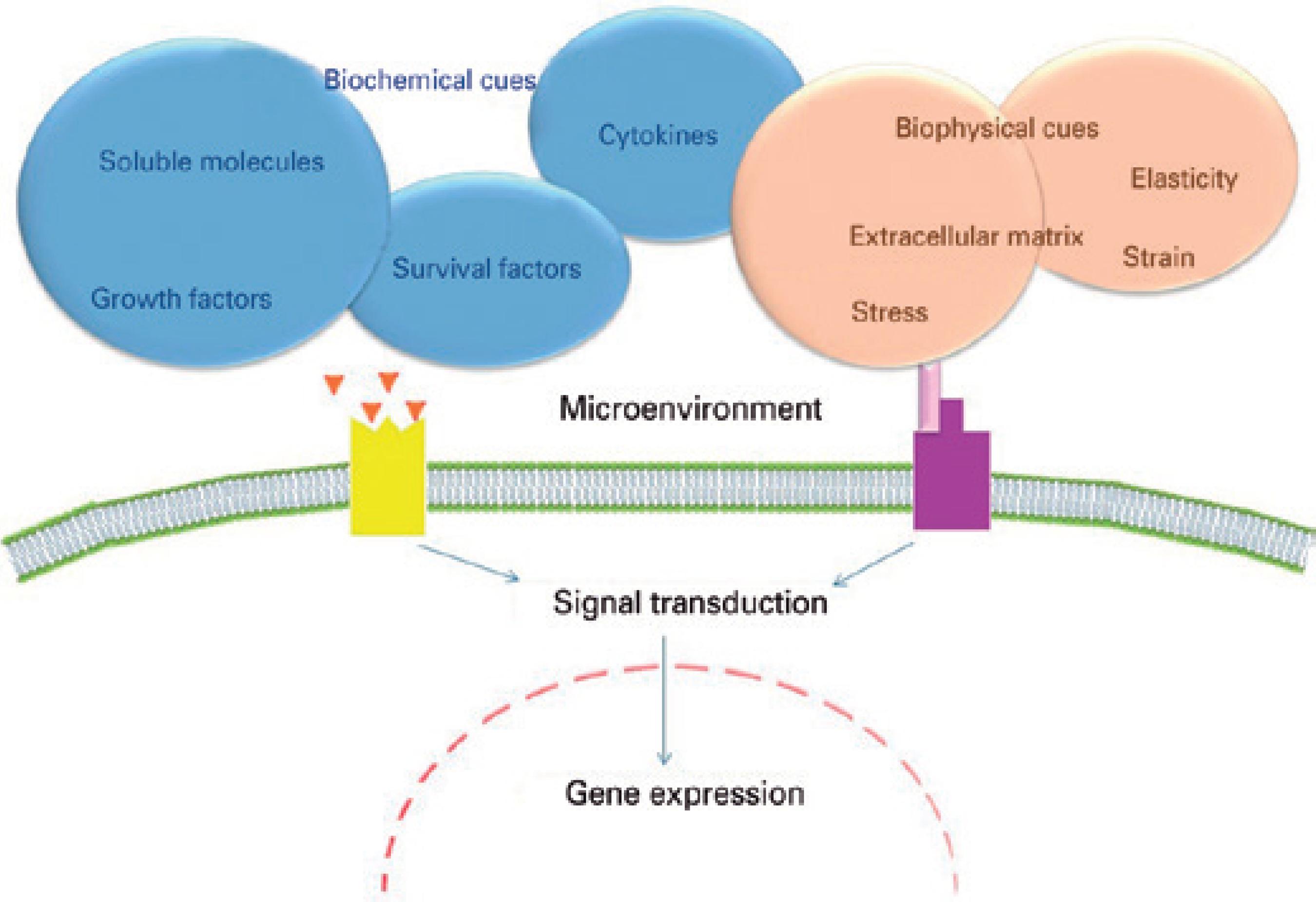
Figure 2 The microenvironmental stimuli that regulate stem cell fate. The stimuli are dictated by the niche, which provides biochemical cues (growth factors, cytokines, survival factors, and permeable small molecules) and biophysical and mechanical cues (strain, stress, and elasticity) related to the extracellular matrix.
One important aspect related to limbal integrity that has received surprisingly little consideration when evaluating the niche regulation of limbal epithelial SCs, or the migration of early TACs from the limbus to the cornea, is the supramolecular nature of the BM and stroma. Both the BM and the stroma are supramolecular organizations (or supraor ga nizations) of ECM; this means that their structural components only play a role in biological processes after forming macromole cular complexes such as microfibrils, fibrils, fibers, lamellae, and networks54. Supraorganization occurs through self-recognition and the genetically encoded self-assembly of biological particles at various structural scales, such as from molecule to macromolecule and from macromolecule to supramolecular structure54.
Supramolecular organizations of ECM are not inert solids (because they can undergo remodeling), and clearly they are not gases54,55. We recently proposed that the limbal epithelial SC extracellular niche should be considered a physiologically and optically active liquid crystalline superstructure54. The concept of biological liquid crystals has already been applied to supraorganized structures and tissues, such as the cornea56, chordae tendineae55, bone57,58, and tendon59. Support for the concept comes from the observation that structural elements from the ECM possess mesophase characteristics58,60. For example, after acidic extraction and in vitro precipitation, fibrillar type I collagen, a major component of corneal and limbal stroma, forms a twisted liquid crystal-like supramolecular gel58,61,62. In addition, sections of corneal and limbal tissues observed between two crossed-polarizers behave as multilayer cholesteric crystals54,56. Furthermore, excised cornea illuminated with polarized light displays dark cross-shaped figures with peripheral concentric colored bands63,64; these are identical to the isogyres observed in uniaxial liquid crystals.
The functional dynamicity of a liquid crystalline and supramole cular biological organization is governed by the reversibility and lability of its covalent and hydrogen bonds and the hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions that connect its components65-68. Supraor ganizations of ECM are therefore able to respond with nanoscale macromolecular reorganization to a series of demands or agents, including an external force (such as strain or compression), piezo- and pyroelectricity, protein binding (e.g., growth factors), enzymatic activity (e.g., metalloproteases), and interaction with mesenchymal, epithelial, and inflammatory cells55,65-68. In this respect, it is widely accepted that corneal and limbal supraorganized ECMs undergo continuous readjustments to their functions of metabolism, turnover, wound healing, and other functional demands. Such readjustments could allow the basal epithelial cells and the epithelial crypts to receive a combination of multiple stimuli and/or sensations within a spatiotemporal context.
Biophysical cues from the supramolecular extracellular matrix
Our sensation of space and movement is routinely predicated on varying physical environment features (such as the clarity of air) that help dictate our behavior in a particular situation. In an analogous manner, evidence suggests that cell responses to microenvironmental stimuli are processed in accordance with transient biophysical cues related to the dynamic supraorganization, topography and movement of ECM22-27.
Biophysical and mechanical cues (or features) from the supramo lecular ECM can be contextualized mainly in terms of compression, pressure, shear, stiffness, force, stress, tension, compliance, rigidity, and elasticity69 (Table 1). It appears that distinct cellular responses may be obtained only by altering one or more of these parameters22-27.
Table 1 Description of the terminology of the biophysical and mechanical cues related to supramolecular organization of extracellular matrix(69)
| Tension, compression, pressure and shear | |
| These terms refer to distinct types of forces and stresses. A cell can attempt to contract using myosin motor, however, be unable to do so because it is attached to an inflexible substrate. In this case, the cell is in tension. In contrast, a compressive force would act to decrease the length of the cell. Pressure is a three-dimensional compressive stress but, unlike other forms of stress, is isotropic. Shear-forces refer to those that act in-plane to the local experiencing the force (as opposed to tension and/or compression, which acts perpendicular to that plane). | |
| Force and stress | |
| Force is a vector defined with accelerating a mass and, in researchs with cells, is either applied to elicit a response or is quantified to evaluate a mechanical reaction from cells. Stress, by contrast, speaks of a force per unit area. | |
| Stiffness, compliance, rigidity and elasticity | |
| Stiffness describes material stiffness, which is an inherent property of the material itself. Compliance is the inverse of stiffness. Rigidity is used synonymously with stiffness, although it traditionally refers to a spring (geometry-specific) stiffness. Elasticity is used synonymously with compliance, although its strict usage refers to the degree to which a material is energy storing vs. dissipating. | |
Some local modifications in biophysical cues from supramolecular ECM during tissue remodeling are caused principally by the addition or removal of cells and by changes in the biosynthesis of macromolecules70. Thus, SCs and TACs are constantly subjected to fluctuating external forces from their niches70. Experimental evidence has clearly shown that changes in biophysical cues can elicit intracellular programs that regulate the fate of SCs through integrin-mediated adhesions and the force balance carried across the mechanical continuum of the ECM-integrin-actin cytoskeleton70. Biophysical features of ECM have been shown to regulate the intracellular architecture and to provide information for cell activity22-27. For example, evidence suggests that the differentiation and migration of TACs involved in corneal epithelium homeostasis could result from the minimization of global tension in response to forces exerted by readjustments of stromal ECM54. Studies have demonstrated that cultured corneal limbal epithelial cells can reorganize the cytoskeletal architecture in response to different biophysical features of ECM-like polymeric materials71-73. In addition, it has also been demonstrated that spatial readjustments of ECM induce an anisotropic distribution of mechanical constraints in epithelial cells, which, in response, change their spatial positions to minimize both intra- and intercellular forces74.
Supraorganization creates signaling sites for cell-ECM interactions54. These can either enhance or inhibit the differentiation signs induced by growth factors, cytokines, and other soluble molecules in the vicinity of a cell or adjacent tissue, and can exert direct effects on the cell nucleus through mechanosensors such as ion channels, G-proteins, and integrins (Figure 3)70,75-77. Integrins are the primary mechanosensors involved in mechanotransductive processes. In these processes, stimuli from supramolecular ECM are translated into biochemical signs that result in changes in the mechanical stretching of cytoplasmic proteins and in the expression of genes related to cell proliferation and migration, or to apoptosis70,75-77.
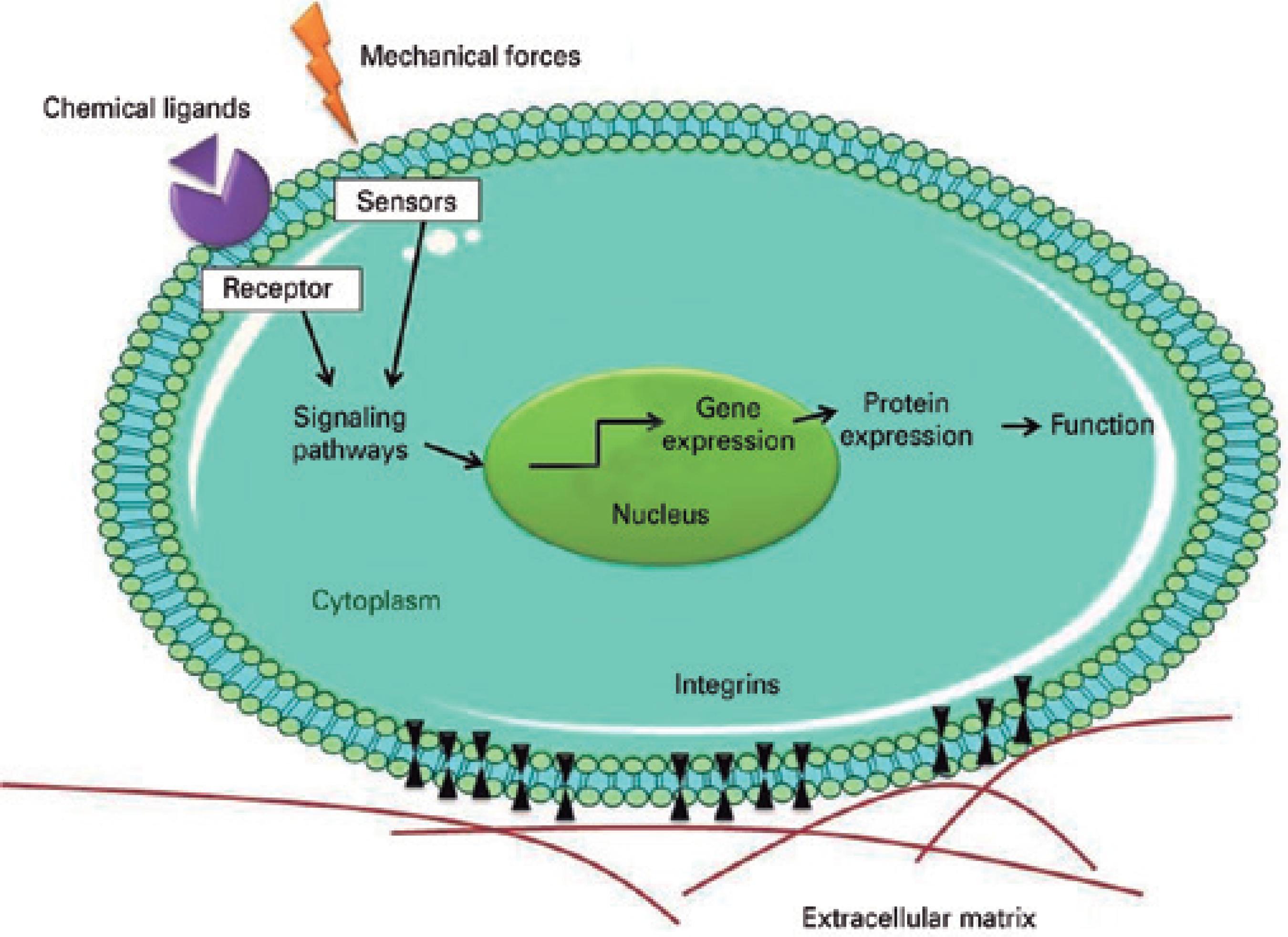
Figure 3 Schematic illustration showing how biophysical cues can stimulate cells through the activation of mechanosensors and integrins. The integrins and sensors activate the intracellular signaling pathways, which in turn activate transcriptional factors and modulate gene expression.
Although the molecular mechanisms by which biophysical cues are translated into biochemical signs remain unclear, it is known that the mechanical stretching of cytoplasmic proteins induces conformational changes in the mechanosensors to activate the binding of other intracellular molecules and to bring about changes in calcium (Ca2+) cellular influx75-77. Calcium has the effect of inhibiting the proliferation and triggering the differentiation of mouse corneal epithelial cells78.
The clinical relevance of knowledge about the supramolecular organization of the extracellular matrix and biophysical cues
The supramolecular organization of ECM and the biophysical re gulation of limbal epithelial SCs may hold the key to engineering stemness and opening up new possibilities for treating the limbal deficiency because they reflect nanoscale morphofunctional characteristics of BM and stromal tissues54. It was with the advent of nanomedicine that the supraorganizations of ECM first the down to be considered among the full set of hierarchic levels that researchers must master to create artificial tissues or membranes54. In bio ma terial sciences, the term "supramolecular organization" is used to refer to the arrangement of biopolymer (ECM components) that confers a structure's macroscopic and biomechanical attributes54. In ophthalmology, three-dimensional printing technology now allows a supraorganization to be evaluated and subsequently reproduced in a laboratory. Research on supraorganization can involve, for example, nanografting, or nanopost and nanopit arrays, with the aim of reproducing the ECM from the nanometer to the micrometer scale.
Understanding the physical cues of a local SC microenvironment is a fundamental step toward understanding the SC itself. The ability of SCs to respond to spatiotemporal changes in the supramolecular arrangement of ECM as well as to distinct mechanical and biophysical cues within their surroundings is gaining increased recognition and will continue to be elucidated in the years to come. An apprecia tion of the supramolecular ECM in the niche can support the de velopment of new biomimetic substrates for the reconstruction of ocular surfaces. In addition, basic knowledge about biophysical and mechanical cues related to supramolecular ECM may enable the therapeutic modulation of endogenous SCs via changes in the microenvironment, as well as provide opportunities to create more effective large-scale artificial culture substrates and bioreactors to expand and differentiate limbal epithelial SCs.




 English PDF
English PDF
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to cite this article
How to cite this article
 Submit a comment
Submit a comment
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Scielo
Scielo
 Pocket
Pocket
 Share on Linkedin
Share on Linkedin

