INTRODUCTION
Behcet disease (BD) is an immune-mediated systemic occlusive vasculopathy for which the etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully clarified. The major symptoms include oral aphthous ulcers and skin and ocular lesions(1). Ocular involvement, which is seen in 60-80% of patients, is characterized by anterior uveitis, posterior uveitis, or panuveitis with retinal vasculitis. In particular, posterior seg ment involvement can significantly affect visual acuity(2-4).
In addition to clinical fundus fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography ultrasound biomicroscopy, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) can be used to evaluate the posterior segment(5,6).
OCT entered clinical use in the late 1990s and made it possible to examine the retinal layers in detail. In 2002, with the introduction of the Stratus OCT instrument, more detailed and high-quality images of the retina could be obtained. By 2006, parallel to developments in OCT technology, spectral domain (SD) OCT began to be used clinically, which made even more detailed evaluations of the retina possible with higher resolution, speed, and contrast(7-10). In this clinical study, we compared the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL), ganglion cell layer (GCL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), and choroid thickness (CT) between patients with BD and healthy subjects by using SD-OCT. Additionally, we compared the OCT parameters, including macular volume (MV), between patients with and without ocular involvement.
METHODS
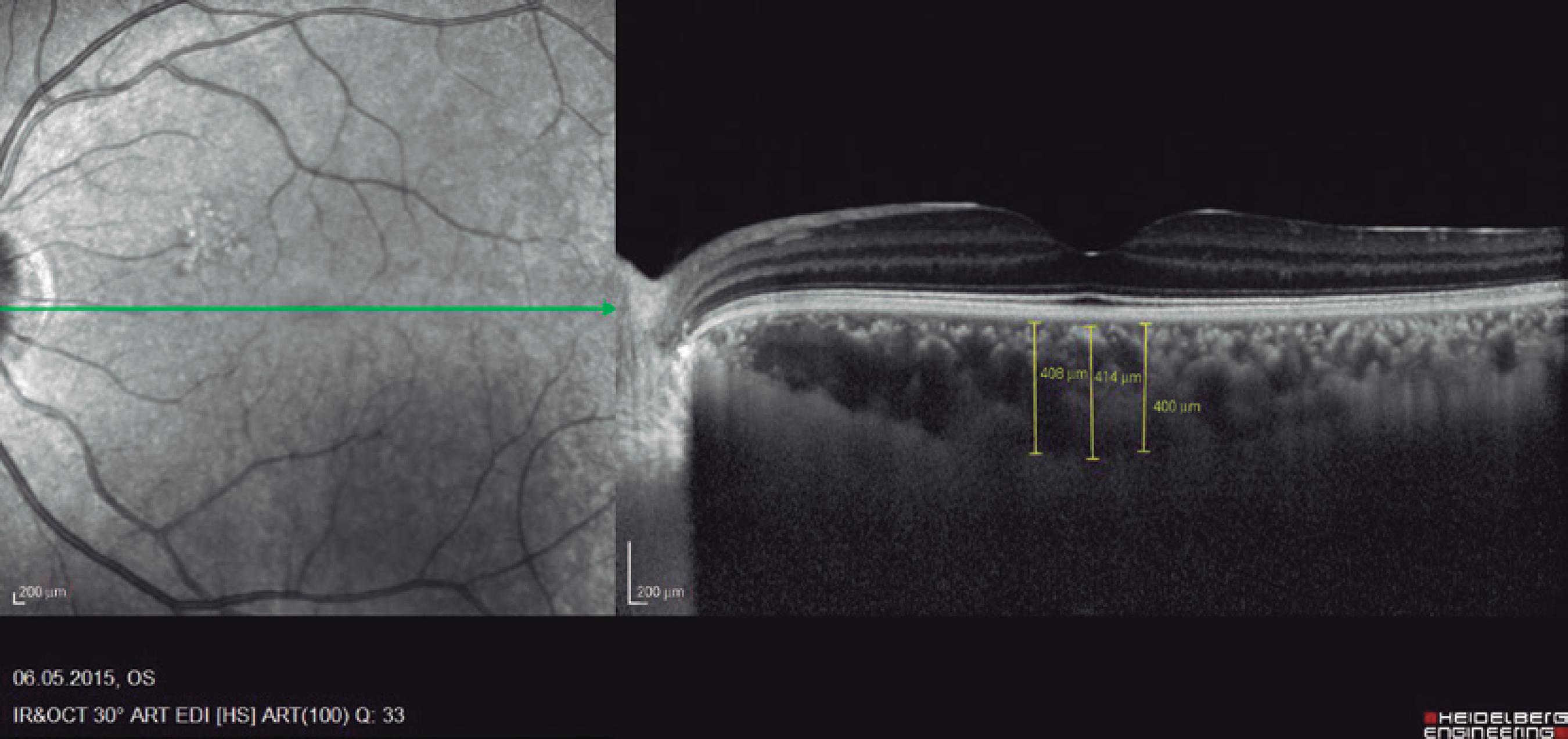
Ninety eyes of 45 healthy subjects and 104 eyes of 52 patients with BD were included in the study. Of the 52 patients with BD, 25 had ocular involvement and 27 did not. The patients without ocular involvement had no history of previous ocular Behçet. This study was approved by the local ethics committee, and the study protocol adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from each patient in both groups. The patients underwent complete ophthalmic examination, including biomicroscopy and fundoscopy. Additionally, OCT measurements were obtained using an SD-OCT device (Spectralis OCT, Version 6.0; Heidelberg Engineering, Germany) with an enhanced depth-imaging mode without pupil dilation. A standardized examination of all subjects was performed. All measurements were performed by the same experienced examiner (ASK) in the morning. RNFL, GCL, IPL, and CT were measured and recorded. The new Spectralis segmentation software was used to obtain RNFL, GCL, and IPL. The SD-OCT choroid layer, RNFL, GCL, and IPL imaging of a normal eye are shown in figures 1,2, 3, and 4, respectively.
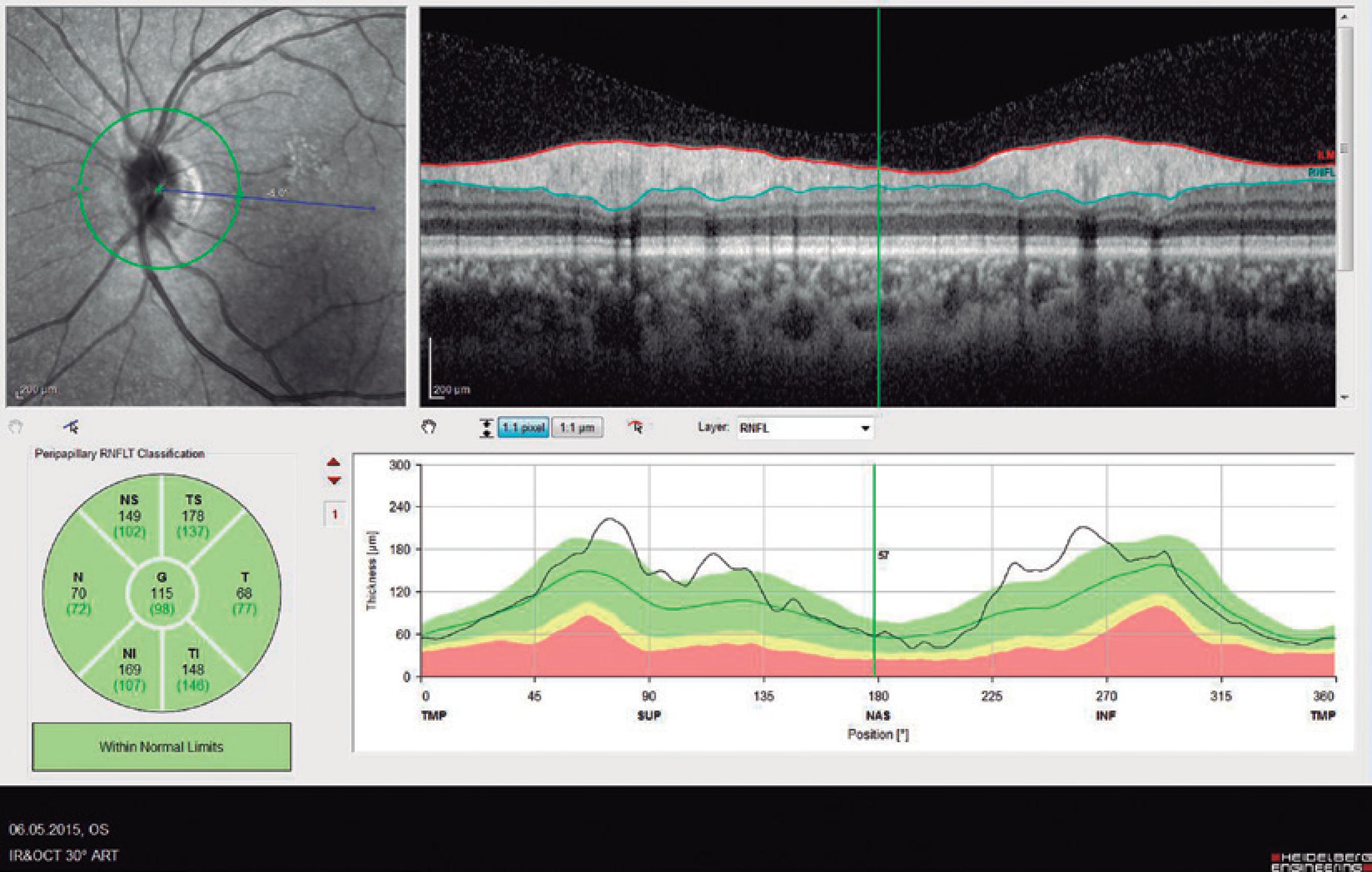
Figure 2 Spectral domain optical coherence tomography retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) imaging of a normal eye.
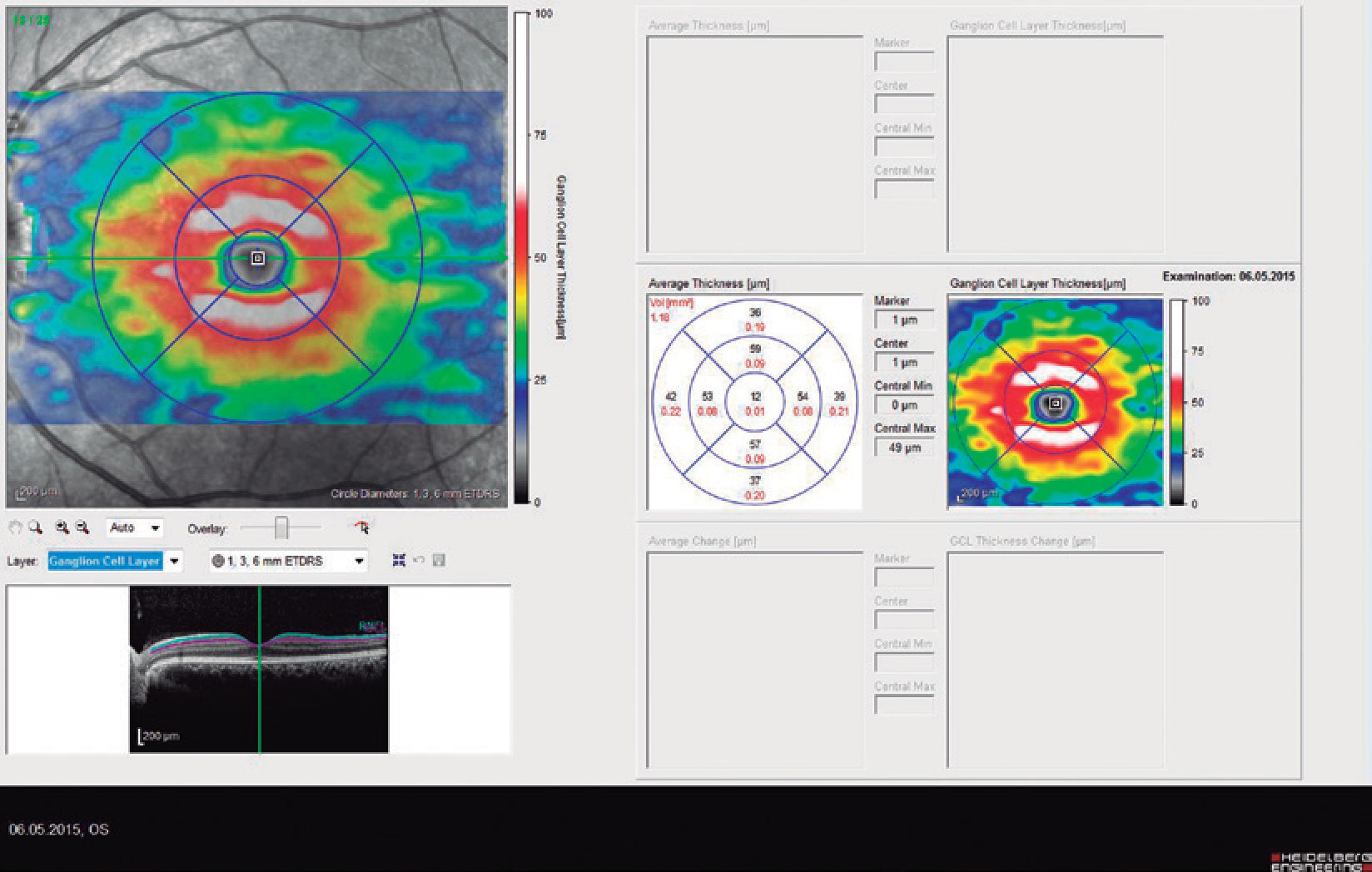
Figure 3 Spectral domain optical coherence tomography ganglion cell layer (GCL) imaging of a normal eye.
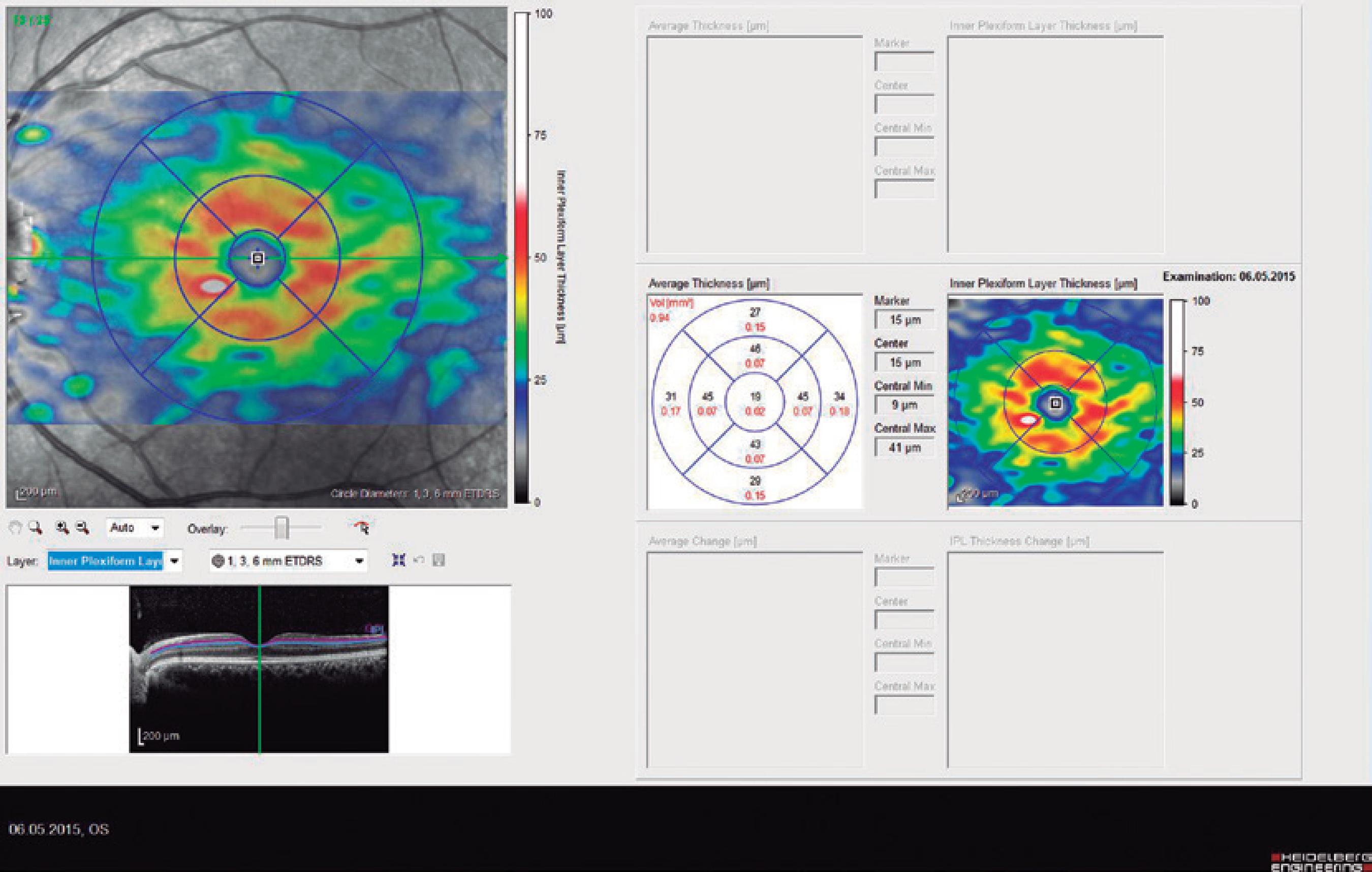
Figure 4 Spectral domain optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer (IPL) imaging of a normal eye
The horizontal cross-sectional view running through the center of the fovea was used to evaluate the central foveal choroidal thickness and 500-µm nasal and 500-µm temporal choroidal thickness to the foveal center. The average of these three location measurements were calculated and compared. The choroidal thickness was manua lly measured from the outer line of the retinal pigment epithelium to the inner border of the sclera using the device's software. A choroidal thicknesss calculation for each subject was performed by two of the co-authors and then averaged for analysis.
In the patients with BD, MV measurements were taken by SD-OCT. Additionally, the rheumatoid factor (RF) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were measured by blood testing in the patients with BD. The exclusion criteria included history of ocular surgery, glaucoma, retinal and macular pathology, diabetes, and uveitis caused by other etiologies. Statistical analysis was performed by using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) 21.0 for windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
Of the 52 patients with BD, 34 (65.4%) were female and 18 (34.6%) were male. Of 45 healthy subjects in the control group, 23 (51.1%) were female and 22 (48.9%) were male. The mean ages of the BD patients and control group were 37.03 ± 10.57 and 39.55 ± 15.94, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in sex and age between the patients and control group (p=0.154 and p=0.356, respectively). Of the 52 patients with BD, 25 (48.1%) had ocular involvement and 27 (51.9%) had no ocular involvement. Of the 25 patients with ocular involvement, 4 had an acute uveitis attack and 21 had chronic uveitis.
A comparison of the mean RNFL, choroid, GCL, and IPL thickness measurements between the 2 groups is presented in table 1. The mean RNFL thickness was significantly lower for the patients with BD than for the control group (p=0.026). The mean choroid thickness measurements were significantly higher in the patients with BD than in the control group (p=0.00). The GCL and IPL thickness measurements were significantly lower in the patients with BD than in the control group (p=0.00).
Table 1 Comparison of OCT parameters between the control group and Behcet disease-patient group
| Group | Mean | Std. deviation | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RNFL | Control group | 107.22 | 8.92 | 0.026 |
| BD group | 104.63 | 13.92 | ||
| Mean choroid | Control group | 245.48 | 28.48 | 0.000 |
| BD group | 330.29 | 78.92 | ||
| GCL | Control group | 1.20 | 0.04 | 0.000 |
| BD group | 1.14 | 0.10 | ||
| IPL | Control group | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.000 |
| BD group | 0.92 | 0.07 |
RNFL= retinal nerve fiber layer; GCL= ganglion cell layer; IPL= inner plexiform layer; BD= Behcet disease.
A comparison of the mean RNFL, choroid, GCL, IPL, and MV thickness measurements between the BD patients with ocular involvement and without ocular involvement is presented in table 2. There were no statistically significant differences in CT, GCL, IPL, RNFL, and MV measurements (p=0.11, p=0.73, p=0.92, p=0.19, and p=0.08, respectively) between the BD patients with and without ocular involvement. There were also no statistically significant differences in the CRP and RF levels (p=0.533 and p=0.102, respectively) between the BD patients with and without ocular involvement.
Table 2 Comparison of OCT parameters, serum RF, and CRP levels beween Behcet disease patients with and without ocular involvement
| Eye involvement | Mean | Std. deviation | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RNFL | No | 106.69 | 16.07 | 0.80 |
| Yes | 102.96 | 11.55 | ||
| Choroid | No | 340.02 | 70.31 | 0.11 |
| Yes | 313.67 | 85.03 | ||
| GCL | No | 1.13 | 00.11 | 0.73 |
| Yes | 1.12 | 00.08 | ||
| IPL | No | 00.92 | 00.08 | 0.92 |
| Yes | 00.91 | 00.05 | ||
| MV | No | 271.47 | 28.80 | 0.08 |
| Yes | 261.64 | 26.07 | ||
| RF | No | 022.37 | 07.82 | 0.10 |
| Yes | 19.42 | 01.02 | ||
| CRP | No | 00.61 | 00.42 | 0.53 |
| Yes | 00.75 | 00.92 |
RNFL= retinal nerve fiber layer; GCL= ganglion cell layer; IPL= inner plexiform layer; MV= macular volume; RF= romatoid factor; CRP= C-reactive protein.
Correlation analyses results are shown in table 3. There was a significant negative correlation between CRP-GCL and CRP-IPL (p=0.006 and p=0.036, respectively). There was also a significant negative correlation between RF-GCL and RF-IPL (p=0.00 and p=0.00, respectively).
Table 3 Correlation between OCT parameters and inflammatory markers in patients with Behcet disease
| GCL thickness | IPL thickness | RNFL thickness | Choroid thickness | Macular volume | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP | r | -0.435 | -0.342 | -0.036 | -0.112 | -0.030 |
| p | -0.006 | -0.036 | -0.832 | -0.511 | -0.859 | |
| RF | r | -0.564 | -0.468 | -0.205 | -0.103 | -0.126 |
| p | -0.000 | -0.003 | -0.216 | -0.544 | -0.457 |
GCL= ganglion cell layer; IPL= inner plexiform layer; RNFL= retinal nerve fiber layer; CRP= C-reactive protein; RF= rheumatoid factor.
DISCUSSION
Behcet disease is an idiopathic, polysymptomatic, chronic, and recurrent systemic vasculitis(1). Although the disease occurs worldwide, its incidence increases from the Mediterranean and Middle East, eastward to Japan(11). It is more common in males, with a male:female ratio of 2:1, but this ratio is reversed in the US and European countries(11). In our BD group, there were more female patients than male patients. Studies have shown that HLA-B5 and HLA-B51 are related to BD(12). In the disease etiology, toxic exposure, infective agents, genetic factors, chromosomal anomalies, IL-8 polimorphism, T-cell CD-4+ type 1 polarization, and auto-immunity have been considered as factors(13-15). However, there is insufficient evidence to support any of these etiological factors. Although the cause of the disease is unknown, histopathological studies have shown that accumulation of immuno-complexes in blood vessel walls activates the complement system and results in vasculitis, which causes tissue damage(16).
In our study, of the 52 patients with BD, 27 (51.9%) had ocular involvement and 25 (48.1%) did not. Of the 27 patients with BD and ocular involvement, 4 (7.7%) patients had acute uveitis attacks and 21 (40.4%) had chronic uveitis. BD usually affects both eyes asymmetrically but rarely, unilateral involvement may be seen. In 80% of the cases with unilateral involvement, the other eye becomes involved within 5 years. Unilateral involvement is more likely associated with HLA-B27+ uveitis. In 20% of the patients with BD, the eye is the first organ to be affected. The rate of eye involvement in patients with BD varies between 50% and 90%. Eye involvement is usually seen after 2 years of oral involvement, but it may take years in some cases. BD can affect the anterior and posterior segments of the eyes separately or jointly(17). Recently, with SD-OCT, image resolution, imaging speed, and sensitivity has improved, and high-quality 3-dimensional images that show all the retinal layers in detail can be obtained(18-20). Consequently, ocular involvement in patients with BD has become an important tool for follow-up.
The retina, which consists of receptors, ganglion cells, glial cells, and axons, is accepted as an extension of the brain by many anatomists. In this aspect, it is thought that the retina is a clearly visible part of the brain. Although the retina does not contain myelin, its ganglion cell neurons and axons make it an ideal model of neuronal tissue. Considering the hypothesis above, in this study, we used OCT to investigate RNFL to show possible degeneration in the retinal nerves of patients with BD without neurological involvement and compared the results with those of healthy subjects. In our study, the mean RNFL thickness was significantly lower for the patients with BD than for the control group. In the literature, there are a few studies about RNFL thickness measurements made by SD-OCT in BD patients with and without ocular involvement. Oray M et al. reported that there was no significant difference in RNFL thickness between BD patients with and without ocular involvement(21). Consistent with this previous study, we did not find a statistically significant difference in RNFL measurements between BD patients with and without ocular involvement.
To our knowledge, no study has reported GCL and IPL thickness measurements in patients with BD. In our study, GCL and IPL thickness measurements were significantly lower in the patients with BD than in the control group (p=0.00 and p=0.00, respectively). In the patients with BD, there were no statistically significant differences in GCL and IPL measurements between the patients with and without ocular involvement. Some studies have reported that fundus examination and photographs can detect RNFL damage following the loss of 50% of ganglion cells(22,23). Measuring GCL and IPL thickness is an important and easy way to detect ganglion cell damage in the early phase during follow-up.
The choroid is one of the most vascularized tissues in the human body; it has important roles in the perfusion of outer retinal layers, thermo-regulation of the retina, maintenance of the anatomical position of the retina, removal of residues, and secretion of growth factors(24). In our study, the mean choroid thickness was significantly higher in the patients with BD than in the control group (p=0.00). Kim et al. reported that subfoveal choroidal thickness measured by enhanced depth imaging -OCT was higher in patients with BD with ocular involvement than in the healthy control group(25). In the same study, subfoveal choroid thickness was higher in the patients with BD with ocular involvement than in the patients with BD without ocular involvement. Additionally, subfoveal choroid thickness was higher in the affected eye than in the other eye in the patients with BD with unilateral ocular involvement. In our study, there was no statistically significant difference in choroid thickness between the BD patients with and without ocular involvement (p=0.11). It has been shown that leakage from vascular structures is responsible for the thickening of the choroid(25). In studies on patients with BD with inactive posterior segment involvement, subfoveal choroidal thickness and retinal thickness were significantly thinner than in those of a healthy population. These studies reported that failure of the choroid to support oxygen and the metabolites in the retina, caused by choroidal atrophy and affected choroidal circulation secondary to recurrent posterior uveitis, were the main reasons for the decrease in subfoveal choroidal and retinal thickness(26-27).
It has been shown that pro-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1, IL-1RA, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-15, IL-17, IL-18, T cells, and neutrophil hyper-activation are etiological factors(28-30). Although increases in CRP and RF levels, which are indicators of inflammation, can be expected, we could not find a statistically significant difference in the CRP and RF levels between the BD patients with and without ocular involvement (p=0.533 and p=0.102, respectively). However, there was a significant negative correlation between CRP-GCL and CRP-IPL. As inflammatory indices increase, GCL and IPL decrease significantly, which may be indicative of the toxic effects of the inflammatory process on retinal nerve layers in patients with BD.
In conclusion, BD itself, even without neurological involvement or eye involvement, may independently cause retinal nerve degeneration, such as a decrease in GCL and IPL and an increase in choroidal thickness. OCT makes it possible to examine the retinal layers in detail. In this aspect, OCT is a useful, inexpensive, and non-invasive tool for detecting retinal nerve degeneration and choroidal changes in patients with BD, even without ocular involvement.




 English PDF
English PDF
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to cite this article
How to cite this article
 Submit a comment
Submit a comment
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Scielo
Scielo
 Pocket
Pocket
 Share on Linkedin
Share on Linkedin

