INTRODUCTION
Trypan blue (TB) is used to facilitate the creation of a continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis during cataract surgery(1,2). Several methods have been used to assess the toxic effects of TB on corneal cells: the concentration-related effect of TB on corneal cell viability; the effects of duration of exposure to TB on cell survival; the effect of the vehicle on the degree of TB toxicity; and the damage caused by (experimental) manipulation of cells or endothelia(3).
Several experimental and clinical studies have tested the cytotoxicity of TB on various ocular anterior segment structures during cataract surgery, and all have demonstrated good biocompatibility for conventional intracameral application of TB 0.1%. However, in vitro studies have demonstrated toxicity of TB to corneal endothelium and corneal fibroblasts at higher concentrations and longer exposure times(4-7). Briefly, at commonly used concentrations, both during cataract surgery and in corneal tissue banks, TB is harmless to corneal cells. However, at higher concentrations or longer exposures, extreme caution is warranted.
Oxidative stress is believed to be a central mechanism of the cellular damage affecting all organs and tissues. Oxygen-derived free radicals appear to be responsible for injury to various organs, and apoptosis mediated by oxidative stress is well established(8-11). Considering the controversial safety results of TB on corneal tissue mentioned above, the current study aimed to further investigate the possible toxic effects of TB using oxidative stress parameters and the degree of apoptosis in corneal tissue.
METHODS
Animals and experimental groups
Thirty adult male Wistar Albino rats, aged 4-8 weeks and weighing 180-200 g each, were used. Animals were housed under continuous observation in appropriate cages under ambient temperature (21 ± 2°C) and humidity (60% ± 5%) with a 12-h light:dark cycle. The animals were housed five per cage and fed a commercial standard diet with water ad libitum. All experiments in the present study were performed in accordance with the “Principles of Laboratory Animal Care” and were approved by the Ethical Committee on Human and Animal Research at Harran University, Sanliurfa, Turkey.
Rats were randomly assigned to three groups of 10 rats each as follows: the sham group (Group 1) (n=10); the control group (Group 2) (n=10), which was administered 0.01 cc balanced sterile salt solution (BSS); and the treatment group (Group 3) (n=10), which was administered 0.006 mg/0.01 cc TB.
The total antioxidant status (TAS) and total oxidant status (TOS) were measured in corneal tissue and blood, and the oxidative stress index (OSI) was calculated. Corneal tissue histopathology was evaluated using caspase-3 and caspase-8 staining, and apoptotic activity was assessed.
Surgical procedures and tissue preparation
Intracameral injection technique
Before the intracameral injection, the rats were aseptically anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of 50 mg/kg ketamine (Ketalar; Parke Davis, Eczacibasi, Istanbul, Turkey) and 10 mg/kg xylazine (Rompun; Bayer AG, Leverkusen, Germany). Topical anesthetic drops (0.5% proparacaine) were applied to the rats’ eyes 10 min before injection. The globe was then detached from the edge of the limb using horizontal angled conjunctival forceps with teeth; anterior chamber injections, tangential to the limbus, were then administered at 3 o’clock using an insulin syringe [0.30 x 8 mm (30-G x 5/16’’) (Ayset Medical Products Industry Co., Adana, Turkey)] under guidance using a YZ20T9 microscope (Nanjing, Redsun Optical Co., Ltd. Jiangsu, China). Group 1 received no injection; Group 2 received intracameral BSS (0.01 cc) [Industrıa Farmaceutica Galenica Senese Materino d’Arbia (SI), Italy]; and Group 3 received intracameral TB (0.006 mg/0.01 cc) (Bio-Blue, Biotech Ophthalmics Pvt. Ltd, Gujarat, India). After 7 days, two rats in Group 2 and one rat in Group 3 had died.
After 7 days, rats were again anesthetized before enucleation. To reach the back of the globe, pressure was applied to the edge of the limb using conjunctival forceps and enucleation was performed using corneoscleral scissors. Following enucleation, the bulbus oculi was removed, after which all animals were euthanized by exsanguination. Round corneal specimens were removed via a limbal incision using a 15º corneal blade; the histopathological specimens were placed in 10% formaldehyde and the biochemical specimens were placed into dry boxes. Last, a 3-cm midline abdominal incision was made and 1.5 cc of blood was drawn from the inferior vena cava. The tissue and blood samples were stored at -70ºC until measurement of TAS and TOS activity.
Repeatability of the experimental results: With regard to the repeatability of this experimental result (i.e., whether it is sufficiently repeatable in different trials), the experimental protocol does not involve any different techniques compared with previously published studies, which will help to improve the stability and repeatability of the experimental results.
Caspase-3 and -8 staining
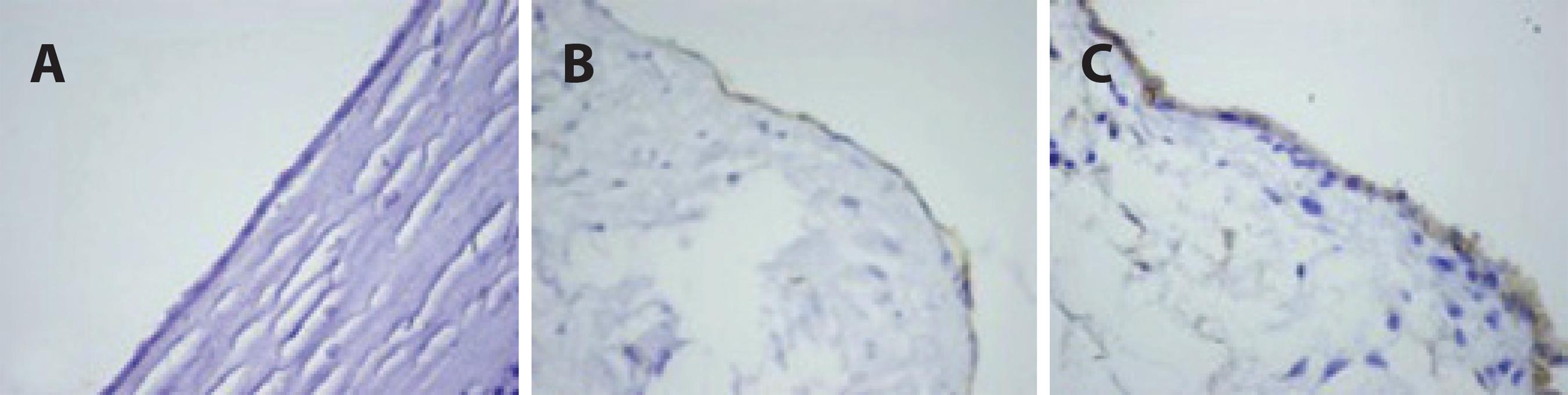
The samples were fixed with 10% formaldehyde and 4 µm thick specimens obtained from paraffin blocks were stained using a standard streptavidin-biotin immunoperoxidase method with anti-caspase-3 (cleaved) (Clone: N/A, Catalog No: PP 229 AA, Biocare Medical) and -caspase-8 antibodies (Clone: C502S, Catalog No: GTX59555, Gene Tex). Tonsillar tissue was used as a positive control, and all specimens were evaluated using light microscopy (Olympus BX51TF, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Also, immunohistochemical staining was evaluated semi-quantitatively using a scale from 0 to 3, on which negative staining was rated 0, weak staining was rated 1, moderate staining was rated 2 and intense staining was rated 3.
TAS
The TAS of supernatant fractions was determined using a novel automated measurement method developed by Erel(12). This method produces the hydroxyl radical, the most potent biological radical. In the assay, ferrous ion solution, present in Reagent 1, is mixed with hydrogen peroxide, present in Reagent 2. The resulting radicals, such as a brown-colored dianisidinyl radical cation produced by the hydroxyl radical, are very potent. Using this method, the anti-oxidative effect of the sample against the potent free radical reactions, which are initiated by the produced hydroxyl radical, is measured. The assay yields precision values <3%. The results are expressed as nmol Trolox equivalents/mg protein.
TOS
The TOS of supernatant fractions was determined using a novel automated measurement method developed by Erel(13). The oxidants in the sample oxidize the ferrous ion-o-dianisidine complex to a ferric ion. The oxidation reaction is enhanced by glycerol in the reaction medium. The ferric ion creates a colored complex with xylenol orange in an acidic medium. The color intensity can be measured spectrophotometrically and is related to the total amount of oxidant molecules present in the sample. The assay is calibrated using hydrogen peroxide, and the results are expressed in terms of nmol H2O2 equivalents/mg protein.
OSI
The OSI was defined as the ratio of TOS to TAS levels. For calculations, TAS units were converted to mmol/L, and the OSI was calculated according to the following formula: OSI (arbitrary units) = TOS (μmol H2O2 equivalents/L)/TAS (mmol Trolox equivalents/L)(12,13).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows software, version 17.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA), and non-parametric independent group comparisons were performed. Data were expressed as medians, minimums and maximums. The Kruskal-Wallis was used for multiple comparisons between groups and the Mann-Whitney test was used if statistical significance was found. A two-sided p value <0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
RESULTS
The TAS, TOS and OSI levels of the blood samples and corneal tissues are presented in tables 1 and 2. The TAS, TOS and OSI levels in the blood samples were not significantly different among the groups (p>0.05 for all). The OSI levels in corneal tissue were significantly different in the TB group compared with the sham and control groups (p<0.05 for all); however, no significant difference was found between the control and sham groups (p>0.05 for all). Additionally, immunohistochemical staining for caspase-3 and -8 showed higher apoptotic activity in the TB group than in the sham and control groups (Tables 3 and 4; Figures 1 and 2).
Table 1 Biochemical oxidative stress parameters
| Sham group (n=10) | Control group (n=8) | Trypan blue group (n=9) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAS (mmol Trolox equivalents/L) | 1.00 ( 0.90, 1.13) | 1.00 ( 0.90, 1.48) | 1.00 ( 0.91, 1.18) | 0.890 |
| TOS (μmol H2O2 equivalents/L) | 28.65 (16.20, 53.12) | 39.15 (15.21, 69.42) | 22.13 (15.21, 70.34) | 0.112 |
| OSI (arbitrary units) | 2.85 ( 1.79, 6.10) | 4.29 ( 3.00, 6.10) | 3.24 ( 2.11, 5.96) | 0.109 |
The variables expressed as median (minimum, maximum). The Kruskal-Wallis test was used; TAS= total antioxidant status; TOS= total oxidant status; OSI= oxidative stress index.
Table 2 Corneal tissue oxidative stress parameters
| Sham group (n=10) | Control group (n=8) | Trypan blue group (n=9) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAS (mmol Trolox equivalents/L) | 0.28 (0.14, 0.44) | 0.52 (0.17, 0.97) | 0.25 (0.16, 0.29) | 0.068 |
| TOS (μmol H2O2 equivalents/L) | 5.13 (2.67, 9.51) | 4.18 (1.38, 8.25) | 4.01 (1.98, 4.73) | 0.125 |
| OSI (arbitrary units) | 1.27 (1.01, 1.71) | 1.35 (1.02, 1.96) | 1.82 (1.48, 2.04)¥, £ | 0.002 |
The variables expressed as median (minimum, maximum). Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests were used; TAS= total antioxidant status; TOS= total oxidant status; OSI= oxidative stress index; Trypan blue vs sham
¥= p=0.001; Trypan blue vs control
£= p=0.012.
Table 3 Immunohistochemical staining for caspase-3
| 0 | + | ++ | +++ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham group | 9 | 1 | - | - | 10 |
| Control group | 7 | 1 | - | - | 8 |
| Trypan blue group | 4 | 4 | 1 | - | 9 |
Table 4 Immunohistochemical staining for caspase-8
| 0 | + | ++ | +++ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham group | 9 | 1 | - | - | 10 |
| Control group | 6 | 2 | - | - | 8 |
| Trypan blue group | 3 | 4 | 2 | - | 9 |
DISCUSSION
The present study yielded intriguing results and, to our knowledge, is the first report of the safety of intracameral TB in corneal tissue using oxidative stress parameters and apoptotic activity. The present study showed that although intracameral TB does not exert a systemic effect, it might be locally toxic to corneal tissue.
Clinically, TB is commonly used at 0.06% or 0.10%, and is instilled into the anterior chamber for 1 min, with or without air or an ophthalmic viscosurgical device, before washout(14). Most studies investigating potential TB toxicity have examined the effects of TB on corneal cells in vitro(1,3,4,15,16). Panda et al. included 205 eyes of 205 patients that had undergone phacoemulisification of cataracts or corneal opacities(17). The authors revealed that TB (0.06%) dye-assisted capsulorhexis was successfully completed in all eyes and the patients were followed up at day 1, day 7, and one and three months postoperatively. Also, some studies found good biocompatibility at incubation times of up to 15 min and concentrations up to 0.40%, indicating that TB is safe for corneal endothelial cells(3,4,15,18-21). Chung et al. also evaluated the safety of TB 1% for assisting visualization of the anterior capsule during phacoemulsification of a mature cataract, and found it to be safe(22). Moreover, Norn reported the perioperative use of this dye (at 0.1%) for the staining of corneal endothelium in anterior segment surgery. No ocular complications were found during eight years of follow-up. Additionally, Melles et al. advocated the use of TB (0.1 mL of a 0.06% solution) to visualize the anterior capsule in cataract surgery(1,15).
Although the safety of TB is well established, it is not without reports of toxicity. Several animal studies have indicated that TB has teratogenic and carcinogenic potential(16,23,24). In animal studies, increasing the concentration from that used clinically (0.006 mg) to 0.017% resulted in a 38% reduction in endothelial cell viability using generic TB and 15% using the proprietary TB. When the concentration was increased to 0.05%, viability decreased by 55% with generic TB, and by 30% with the proprietary TB. A study performed using corneal fibroblasts and endothelial cells in human donor eyes demonstrated a TB-induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effect after incubation times of up to 24 h. High TB concentrations and long incubation times have also been shown to exhibit significant cytotoxicity in human cultured corneal endothelial cells(14,25).
Given these findings, controversy exists over whether TB is safe for corneal tissue. In our study, we detected no systemic effects using oxidative stress parameters from blood samples; however, caspase-3 and -8 staining demonstrated increased apoptotic activity in the corneal tissue samples, and levels of oxidative stress markers were also increased.





 English PDF
English PDF
 Print
Print
 Send this article by email
Send this article by email
 How to cite this article
How to cite this article
 Submit a comment
Submit a comment
 Mendeley
Mendeley
 Scielo
Scielo
 Pocket
Pocket
 Share on Linkedin
Share on Linkedin

