

Amanda Ginelli; Nicole Bulgarão Maricondi de Almeida; Newton Kara-Júnior
DOI: 10.5935/0004-2749.2024-0405
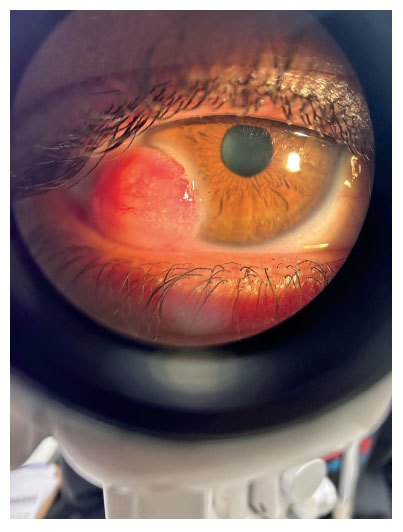
Corneal dermoid (Figure) is a congenital benign tumor and ocular malformation(1) generally classified into three grades of severity(2), with the most common site being the right eye’s temporal limbus(1). Corneal dermoid can result in visual impairment, restricted eye movement, and facial asymmetry(1). Pathological features include squamous epithelium coverage, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and adipose and fibrous tissue(1). Surgery is effective(1), although complications include persistent epithelial defects and peripheral corneal vascularization and opacity(2).
REFERENCES
1. Xuan S, Pei X, Li Z. A Retrospective analysis of corneal dermoid. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e64840.
2. Wan Q, Tang J, Han Y, Ye H. Surgical treatment of corneal dermoid by using intrastromal lenticule obtained from small-incision lenticule extraction. Int Ophthalmol. 2020;40(1):43-9.
Submitted for publication:
December 16, 2024.
Accepted for publication:
December 17, 2024.
Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in this study.
Funding: This study received no specific financial support.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.