

Andréa Santucci; Nicole Bulgarão Maricondide Almeida; Newton Kara-Junior
DOI: 10.5935/0004-2749.2024-0389
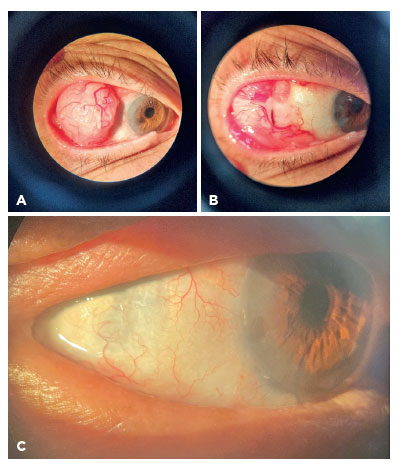
Conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma (A) is one of the most common ocular tumors. It is typically a unilateral tumor with slow, progressive growth and rare metastasis. Risk factors include ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure, smoking, human papillomavirus infection, and human immunodeficiency virus infection(1). Treatment options may involve topical chemotherapy agents and immunomodulatory drugs like 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (B)(2). Intraocular invasion after primary treatment is uncommon and may be prevented by adjuvant brachytherapy following tumor resection (C)(3).
REFERENCES
1. Cruzado-Sánchez D, Salas-Diaz M, Tellez WA, Alvarez-Matos SE, Serpa-Frías S. Interferon alpha-2a as alternative treatment for conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2017;92(11):539-42. English, Spanish.
2. Yeoh CH, Lee JJ, Lim BX, Sundar G, Mehta JS, Chan AS, et al. The management of ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN). Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):713.
3. Cano-Suárez MT, Saornil-Álvarez MA, García-Álvarez C, López-Lara F, Frutos-Baraja JM, García-Lagarto E. Infiltrative intraocular conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma after local resection and brachytherapy: clinical and pathological findings. Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2017;3(3):216-9.
Submitted for publication:
December 10, 2024.
Accepted for publication:
December 11, 2024.
Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Funding: This study received no specific financial support.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.